Applies to: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2
You can control a remote PC by using a Microsoft Remote Desktop client. The client can run on almost any device, including on your mobile smartphone. The client gives you the same powers you would have if you could reach the PC's keyboard. Through the client, you can:
- Operate the apps that are installed on the PC.
- Access the files and network resources of the PC.
- Leave the apps open when you end the client.
In this article. Applies to: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2. You can control a remote PC by using a Microsoft Remote Desktop client. Description Use the Microsoft Remote Desktop app to connect to a remote PC or virtual apps and desktops made available by your admin. The app helps you be productive no matter where you are. Getting Started Configure your PC for remote access first.
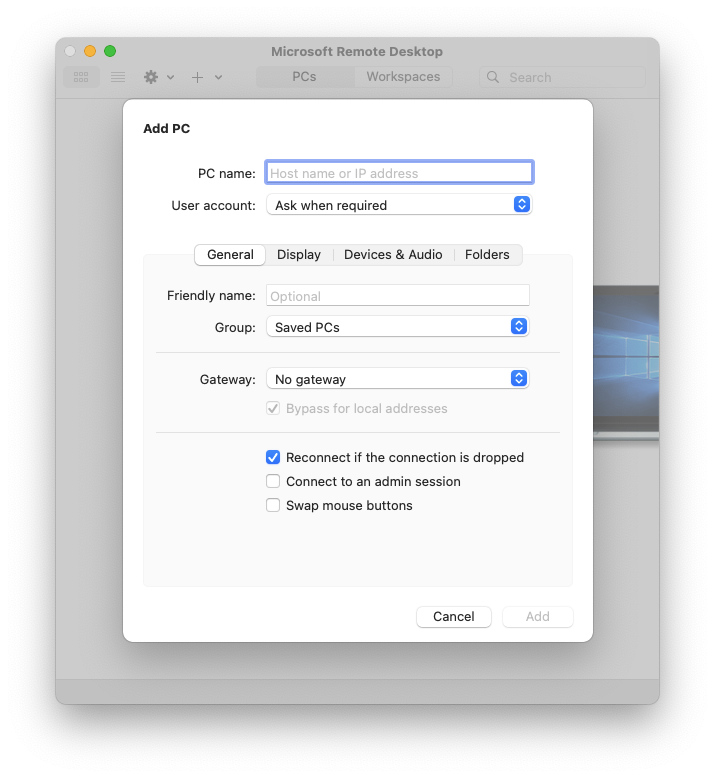
We have remote resources feed at work. Working at v8 but not in v10. It can find all programs and let me run them. But after I have 'Configuring remote connection' stucked on my screen. Did anyone saw such problem in new app already? We have an issue where our RemoteApps work fine with the 8.0.43 client, but will hang at 'configuring remote. Get the Remote Desktop client. Follow these steps to get started with Remote Desktop on your Mac: Download the Microsoft Remote Desktop client from the Mac App Store. Set up your PC to accept remote connections. (If you skip this step, you can't connect to your PC.) Add a Remote Desktop connection or a remote resource. Microsoft Chromebook – Microsoft Remote Desktop Client V10 Setup and Use This setup is only required to setup access to the Virtual Desktop. Students will only do this at the beginning of the semester or if their chromebook has to be repaired.
Before you start, see the supported configuration article. The article discusses the PC configurations that the Remote Desktop clients can connect to. Also see the client FAQ article.
The following client apps are available:
| Client | Get the app | Documentation | Latest version |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Desktop | Windows Desktop client | Get started, What's new | 1.2.1844 |
| Microsoft Store | Windows 10 client in the Microsoft Store | Get started, What's new | 1.2.1810 |
| Android | Android client in Google Play | Get started, What's new | 10.0.10 |
| iOS | iOS client in the App Store | Get started, What's new | 10.2.5 |
| macOS | macOS client in the App Store | Get started, What's new | 10.6.1 |
Configuring the remote PC
To configure your remote PC before accessing it remotely, see Allow access to your PC.
Remote Desktop client URI scheme
You can integrate features of Remote Desktop clients across platforms by enabling a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) scheme. Learn about the supported URI attributes that you can use with the iOS, Mac, and Android clients.
-->This article describes the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) that's used for communication between the Terminal Server and the Terminal Server Client. RDP is encapsulated and encrypted within TCP.
Original product version: Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 186607
Summary

RDP is based on, and is an extension of, the T-120 family of protocol standards. A multichannel capable protocol allows for separate virtual channels for carrying the following information:
- presentation data
- serial device communication
- licensing information
- highly encrypted data, such as keyboard, mouse activity
RDP is an extension of the core T.Share protocol. Several other capabilities are retained as part of the RDP, such as the architectural features necessary to support multipoint (multiparty sessions). Multipoint data delivery allows data from an application to be delivered in real time to multiple parties, such as Virtual Whiteboards. It doesn't require to send the same data to each session individually.
In this first release of Windows Terminal Server, we're concentrating on providing reliable and fast point-to-point (single-session) communications. Only one data channel is used in the initial release of Terminal Server 4.0. However, the flexibility of RDP gives plenty of room for functionality in future products.
One reason that Microsoft decided to implement RDP for connectivity purposes within Windows NT Terminal Server is that it provides an extensible base to build many more capabilities. RDP provides 64,000 separate channels for data transmission. However, current transmission activities are only using a single channel (for keyboard, mouse, and presentation data).
RDP is designed to support many different types of Network topologies, such as ISDN, POTS. RDP is also designed to support many LAN protocols, such as IPX, NetBIOS, TCP/IP. The current version of RDP will only run over TCP/IP. With customer feedback, other protocol support may be added in future versions.
The activity involved in sending and receiving data through the RDP stack is essentially the same as the seven-layer OSI model standards for common LAN networking today. Data from an application or service to be transmitted is passed down through the protocol stacks. It's sectioned, directed to a channel (through MCS), encrypted, wrapped, framed, packaged onto the network protocol, and finally addressed and sent over the wire to the client. The returned data works the same way only in reverse. The packet is stripped of its address, then unwrapped, decrypted, and so on. Finally the data is presented to the application for use. Key portions of the protocol stack modifications occur between the fourth and seventh layers, where the data is:
- encrypted
- wrapped
- framed
- directed to a channel
- prioritized
One of the key points for application developers is that, in using RDP, Microsoft has abstracted away the complexities of dealing with the protocol stack. It allows them to write clean, well-designed, well-behaved 32-bit applications. Then the RDP stack implemented by the Terminal Server and its client connections takes care of the rest.
For more information about how applications interact on the Terminal Server, and what to know when developing applications for a Windows Terminal Server infrastructure, see the following white paper:
Optimizing Applications for Windows NT Server 4.0, Terminal Server Edition
Four components worth discussing within the RDP stack instance are:
- the Multipoint Communication Service (MCSMUX)
- the Generic Conference Control (GCC)
- Wdtshare.sys
- Tdtcp.sys
MCSmux and GCC are part of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) T.120 family. The MCS is made up of two standards:
Remote Desktop Connection Windows 10 Download Free
- T.122: It defines the multipoint services
- T.125: It specifies the data transmission protocol
MCSMux controls:
- channel assignment by multiplexing data onto predefined virtual channels within the protocol
- priority levels
- segmentation of data being sent

It essentially abstracts the multiple RDP stacks into a single entity, from the perspective of the GCC. GCC is responsible for management of those multiple channels. The GCC allows the creation and deletion of session connections and controls resources provided by MCS. Each Terminal Server protocol (currently, only RDP and Citrix's ICA are supported) will have a protocol stack instance loaded (a listener stack awaiting a connection request). The Terminal Server device driver coordinates and manages the RDP protocol activity. It's made up of smaller components:
- an RDP driver (Wdtshare.sys) for UI transfer, compression, encryption, framing, and so on.
- a transport driver (Tdtcp.sys) to package the protocol onto the underlying network protocol, TCP/IP.
Microsoft Remote Desktop V10 App
RDP was developed to be entirely independent of its underlying transport stack, in this case TCP/IP. It means that we can add other transport drivers for other network protocols as customers needs for them grow, with little or no significant changes to the foundational parts of the protocol. They're key elements to the performance and extendibility of RDP on the network.
